Technical Analysis of Cryptocurrencies: An In-depth Exploration
The world of cryptocurrencies has transformed financial landscapes, introducing decentralized assets like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and thousands of altcoins. To navigate these volatile markets effectively, traders and investors rely heavily on technical analysis (TA), a methodology that uses historical price data and trading volumes to forecast future price movements. This article delves deep into the technical analysis of cryptocurrencies, providing a comprehensive understanding of its tools, principles, and practical applications Mastering Technical Analysis for Cryptocurrency.
Foundations of Technical Analysis
Technical analysis rests on three fundamental assumptions:
- Market Discounts Everything: This principle asserts that all relevant information—economic, political, and psychological—is already reflected in the asset’s price. Thus, studying price action suffices to make informed predictions.
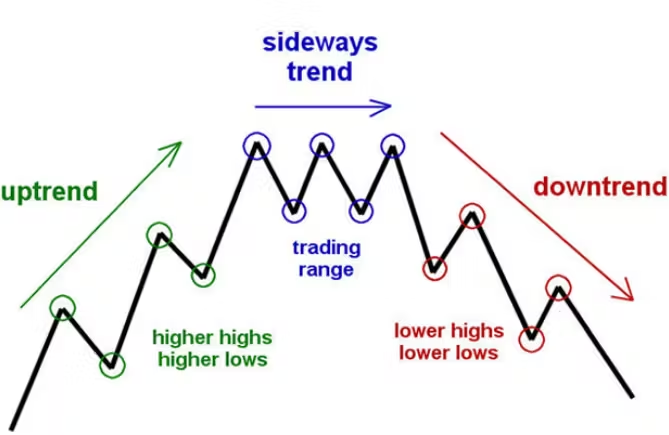
- Price Moves in Trends: Prices follow identifiable trends, whether upward, downward, or sideways. Understanding these trends helps traders align their strategies with market direction.
- History Repeats Itself: Human psychology and market behavior often repeat over time, creating predictable patterns. Technical analysts study these patterns to anticipate future movements.

Key Tools and Indicators
1. Price Charts
Price charts serve as the backbone of technical analysis. The most commonly used types include:
- Line Charts: Simplified charts connecting closing prices over time.
- Bar Charts: Display high, low, opening, and closing prices for each time interval.
- Candlestick Charts: Visually appealing and information-rich, candlestick charts depict open, high, low, and close prices for specific periods, offering insights into market sentiment.
2. Trend Analysis
Identifying trends is essential for formulating trading strategies. Traders use tools like:
- Trendlines: Straight lines connecting significant highs or lows to outline the trend’s direction.
- Moving Averages: Indicators like the Simple Moving Average (SMA) and Exponential Moving Average (EMA) smooth out price data, revealing underlying trends.

3. Support and Resistance Levels
- Support: A price level where buying interest prevents further decline.
- Resistance: A price level where selling interest halts upward momentum.Mastering Technical Analysis for Cryptocurrency
These levels are crucial for predicting potential price reversals or continuations.
4. Volume Analysis
Volume confirms trends and signals strength or weakness in price movements. Higher volumes typically indicate strong trends, while declining volumes suggest waning momentum Mastering Technical Analysis for Cryptocurrency.
5. Oscillators and Momentum Indicators
Oscillators help identify overbought or oversold conditions. Popular indicators include:
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): Measures the speed and change of price movements, indicating overbought (>70) or oversold (<30) conditions.
- Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD): Tracks the relationship between two moving averages, signaling potential buy or sell opportunities Mastering Technical Analysis for Cryptocurrency.
- Stochastic Oscillator: Compares closing prices to price ranges over a specific period, highlighting market momentum.

6. Chart Patterns
Chart patterns are visual formations that indicate potential price movements. Key patterns include:
- Head and Shoulders: A reversal pattern indicating a shift from bullish to bearish trends or vice versa.
- Triangles: Continuation patterns where price consolidates before breaking out in the trend’s direction.
- Double Tops and Bottoms: Reversal patterns signaling a change in the prevailing trend.
7. Fibonacci Retracement
Derived from the Fibonacci sequence, this tool identifies potential reversal levels by dividing key price ranges into ratios (e.g., 38.2%, 50%, 61.8%).
Applying Technical Analysis to Cryptocurrencies
Cryptocurrencies present unique challenges and opportunities for technical analysis due to their high volatility, 24/7 trading, and lack of centralized control. Let’s explore how TA applies specifically to this market:
A. Volatility
Crypto markets experience significant price fluctuations. While this increases risk, it also provides ample opportunities for profit, especially for day traders and swing traders Mastering Technical Analysis for Cryptocurrency.
B. Liquidity
Liquidity varies across cryptocurrencies. Major coins like Bitcoin and Ethereum exhibit high liquidity, ensuring smoother price movements, while smaller altcoins may face sharp price swings due to low trading volumes.
C. Timeframes
The choice of timeframe—ranging from minutes to months—depends on the trader’s strategy. Day traders focus on shorter timeframes, while long-term investors analyze weekly or monthly charts.
D. Market Cycles
Cryptocurrencies often exhibit distinct market cycles characterized by accumulation, markup, distribution, and markdown phases. Recognizing these cycles is crucial for timing entries and exits Mastering Technical Analysis for Cryptocurrency.
Strategies for Technical Analysis
1. Trend Following
Traders use trend-following strategies to capitalize on sustained price movements. Tools like moving averages and trendlines help identify and confirm trends.
2. Breakout Trading
Breakout strategies involve entering trades when prices breach significant support or resistance levels. High volumes accompanying breakouts often indicate strong price momentum.
3. Swing Trading
Swing traders aim to capture short- to medium-term price movements within broader trends. Oscillators like RSI and MACD are invaluable for identifying entry and exit points.
4. Scalping
Scalpers exploit small price changes by executing multiple trades within short timeframes. Precision and discipline are critical for success.
Risk Management in Cryptocurrency Trading
Effective risk management is vital in volatile crypto markets. Key principles include:
- Position Sizing: Allocate a small percentage of your portfolio to individual trades to minimize risk.
- Stop-Loss Orders: Predetermine exit points to limit losses.
- Diversification: Spread investments across multiple assets to reduce exposure to a single cryptocurrency’s volatility.
- Emotional Discipline: Avoid impulsive decisions driven by fear or greed.
Limitations of Technical Analysis
While powerful, technical analysis has its limitations:
- Subjectivity: Interpretation of charts and patterns varies among analysts.
- Lagging Indicators: Many tools, like moving averages, reflect past data and may delay signals.
- Market Anomalies: Unpredictable events like regulatory changes or technological breakthroughs can disrupt patterns.
- Overemphasis on Patterns: Sole reliance on TA without considering fundamental analysis may lead to suboptimal decisions.
Integrating Technical and Fundamental Analysis
Combining technical analysis with fundamental analysis offers a holistic approach to cryptocurrency trading. Fundamental analysis evaluates the intrinsic value of a cryptocurrency by examining factors like:
- Project Utility: The real-world use case of the blockchain.
- Development Team: Credibility and expertise of the project’s creators.
- Community Support: The size and engagement of the cryptocurrency’s community.
- Market Sentiment: Broader public perception and adoption trends.
For instance, using TA to identify optimal entry points after assessing a coin’s long-term potential through fundamental analysis can enhance profitability.
The Future of Technical Analysis in Cryptocurrency
As the cryptocurrency market matures, technical analysis is evolving. Emerging trends include:
- AI and Machine Learning: Advanced algorithms are being developed to analyze market data and predict price movements.
- Decentralized Analytics Platforms: Blockchain-based analytics tools offer transparent and tamper-proof market insights.
- On-Chain Metrics: Indicators derived from blockchain data, like active addresses and transaction volumes, provide additional layers of analysis.
Conclusion
Technical analysis remains an indispensable tool for navigating the complex and dynamic cryptocurrency markets. By mastering its principles, tools, and strategies, traders can make informed decisions and maximize their potential for profit. However, success also requires a balanced approach, integrating risk management and fundamental analysis to navigate the unpredictable nature of the crypto landscape effectively.

Q1: What is technical analysis, and why is it important in cryptocurrency trading?
A1: Technical analysis involves studying historical price data and trading volumes to predict future market movements. In the volatile world of cryptocurrencies, TA helps traders identify trends, optimal entry and exit points, and potential price reversals, enabling informed decision-making.
Q2: What are the three core assumptions of technical analysis?
A2: The three core assumptions are:
- Market Discounts Everything: All information is reflected in the price.
- Price Moves in Trends: Prices follow upward, downward, or sideways trends.
- History Repeats Itself: Human behavior and market patterns are repetitive, making historical analysis predictive.
Q3: What types of charts are used in technical analysis?
A3: Common chart types include:
- Line Charts: Connect closing prices over time.
- Bar Charts: Show high, low, opening, and closing prices for intervals.
- Candlestick Charts: Provide rich information on open, high, low, and close prices, highlighting market sentiment.
Q4: How do traders identify trends in cryptocurrency markets?
A4: Traders use tools like:
- Trendlines: Connecting highs or lows to reveal direction.
- Moving Averages: Smoothing price data to highlight trends. Popular types include the Simple Moving Average (SMA) and Exponential Moving Average (EMA).
Q5: What are support and resistance levels, and why are they important?
A5:
- Support: A price level where demand prevents further decline.
- Resistance: A price level where supply halts upward movement. These levels are crucial for predicting reversals or continuations in price trends.
Q6: Which indicators are most commonly used in technical analysis?
A6: Popular indicators include:
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): Measures overbought (>70) or oversold (<30) conditions.
- MACD: Tracks the relationship between two moving averages to signal buy/sell opportunities.
- Stochastic Oscillator: Highlights market momentum by comparing closing prices to historical ranges.
Q7: What role does volume play in technical analysis?
A7: Volume confirms the strength of trends. High volumes indicate robust price movements, while declining volumes suggest weakening trends or potential reversals.
Q8: How are Fibonacci retracement levels applied in cryptocurrency trading?
A8: Traders use Fibonacci levels (e.g., 38.2%, 50%, 61.8%) to identify potential reversal points during retracements within broader trends. These levels act as support or resistance zones.
Q9: What strategies can traders employ using technical analysis?
A9: Common strategies include:
- Trend Following: Capitalizing on sustained price movements.
- Breakout Trading: Entering trades when prices breach support/resistance levels.
- Swing Trading: Profiting from short- to medium-term price movements.
- Scalping: Executing multiple trades to exploit small price changes.
Q10: What are the risks associated with technical analysis in crypto markets?
A10: Key risks include:
- Subjectivity: Different interpretations of charts and patterns.
- Lagging Indicators: Many tools rely on historical data, delaying signals.
- Market Anomalies: Unpredictable events can disrupt patterns.
- Overreliance on TA: Ignoring fundamental analysis may lead to poor decisions.
Q11: How can traders manage risks in cryptocurrency trading?
A11: Effective risk management involves:
- Position Sizing: Limiting exposure per trade.
- Stop-Loss Orders: Predetermining exit points to minimize losses.
- Diversification: Spreading investments across multiple assets.
- Emotional Discipline: Avoiding decisions driven by fear or greed.
Q12: Can technical analysis be integrated with fundamental analysis?
A12: Yes, combining both approaches offers a comprehensive strategy. Fundamental analysis assesses intrinsic value (e.g., project utility, team credibility), while TA identifies optimal entry and exit points, enhancing profitability.
Q13: How is technical analysis evolving in cryptocurrency markets?
A13: Emerging trends include:
- AI and Machine Learning: Automating data analysis and predictions.
- Decentralized Analytics Platforms: Providing transparent, blockchain-based insights.
- On-Chain Metrics: Utilizing blockchain data, like transaction volumes, for advanced analysis.

Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.